Businesses and manufacturers turn to die casting more often to produce complex metal parts. The process guarantees precision, speed, and efficiency for the most part. Still, is the cost reasonable enough to justify the outcome for your project?
Cost estimation remains a top priority for manufacturers and clients alike. And die casting cost involves several factors to decide on the final pricing. Let’s break down the essential factors to drive die casting costs towards making a more cost-effective choice.
Key Factors to Influence Die Casting Cost Estimation
- Cost of Tooling + Mold Manufacturing
Complex molds with multiple cavities increase upfront tooling expense. A single-cavity mold for small parts may cost $5,000 – $15,000. A multi-cavity mold for automotive components can exceed $50,000.
Features like undercuts, threads, or complex details involve slides and cores. They also add up to 30% to the tooling cost. Precision machining, heat treatment, and appropriate testing add to the high expense.
However, manufacturers can amortize even a staggering amount over production volume. In fact, high-volume runs are more economical; the overall cost gets distributed across thousands of metal parts.
- Part Design (Complexity)
Larger parts need larger molds and heavier machinery. Parts with thinner walls (<2 mm) demand higher precision. Such precision eventually leads to increased scrap risk.
Tight tolerances (±0.05 mm) raise machining and inspection costs. The tighter the tolerance, the higher the price. Ribs, bosses, and threads reduce assembly needs but increase the complexity of casting dies.
Simplified geometry can lower tooling and machining costs. For example, smartphone housings with uniform walls are cheaper than engine blocks with intricate cooling channels.
- Production Volume
High-volume production spreads tooling costs, reducing per-part expense. Not to mention, die casting becomes economical at 10,000+ parts compared to machining or 3D printing.
Tooling dominates the cost in low-volume runs, making alternatives like sand casting cheaper. However, die casting can save up to 50% per part compared to machining in high-volume runs.
- Material Selection
Aluminum comes with a $3.13/kg raw cost. It indeed provides a favorable deal for lightweight parts. Zinc is also cheaper for small precision parts. However, lightweight magnesium is more expensive and harder to source.
Global aluminum prices vary to some considerable extent. China usually offers lower rates than Europe. Scrap rates can vary by part geometry and process control (gating, venting, cooling, and alloy), which can affect overall yield and cost. Zinc die casting enables superior dimensional stability.
- Die Casting Machine Size and Cycle Time
Larger parts require higher-tonnage machines (up to 4,000 tons). Such massive machinery increases the hourly rates. Additionally, higher pressure enables further precision for added energy costs.
Even the cooling time directly affects the cycle speed. Faster cycles can significantly reduce per-part cost. For example, a 30-second cycle vs a 60-second cycle can halve labor and machine costs.
- Labor and Operational Costs
Automated systems reduce labor costs with a higher capital investment. No matter the case, skilled operators are mandatory for proper mold setup and quality control.
Also, labor costs in Asia-Pacific can be up to 50% lower than in Europe or North America.Such a large cost gap can influence partnership decisions for global sourcing.
Still, overhead costs are crucial for efficient production, especially with higher production quantities.
- Secondary Operations and Finishing
Trimming, deburring, and CNC machining of parts can add up to 20% to the existing cost. It may get higher with complex parts. Anodizing, powder coating, or plating can induce $0.50 – $2.00 per part.
Integrated finishing can reduce the assembly cost. However, it still increases upfront mold complexity. Consumer electronics need anodized aluminum, pushing the finishing cost compared to raw castings.
- Quality Standards and Inspection Requirements
Dimensional checks are obligatory to ensure full compliance with ISO standards. Aerospace components undergo non-destructive X-ray or leak testing. Such NDTs induce an additional 10% – 15% to total costs.
The stricter the standards for the parts, the higher the costs. Automotive parts and medical devices go through rigorous inspection before going into service. Such measures also increase per-part expense.
Die Casting Process: Cost Contribution by Factor
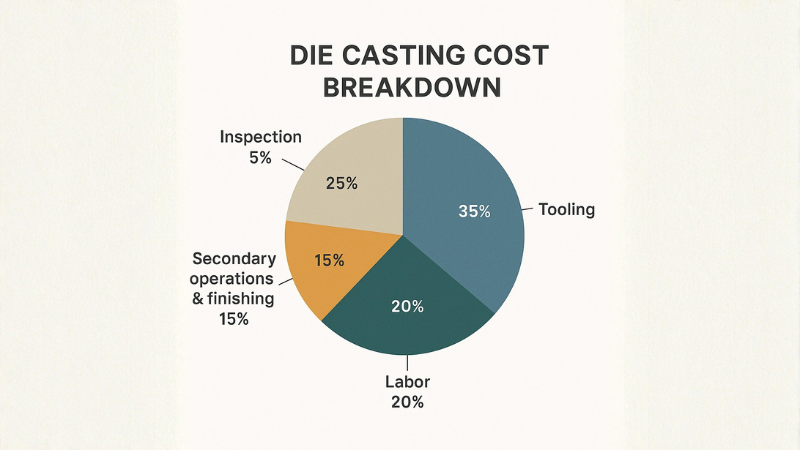
Die Casting Tooling Cost Estimation
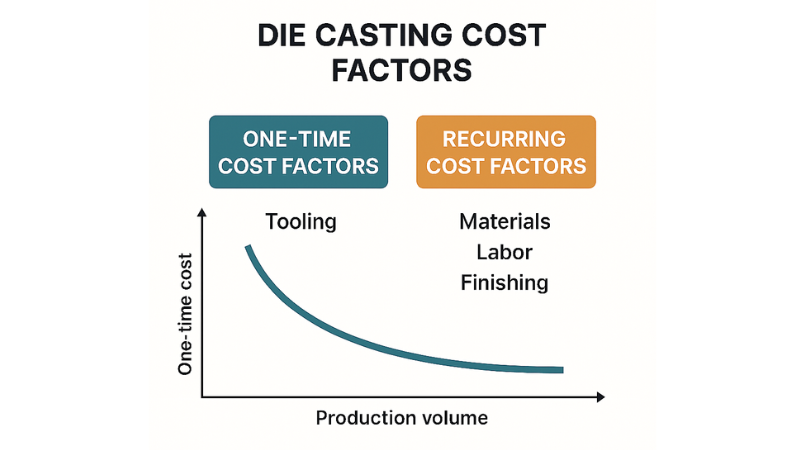
A proper cost estimation takes one-time investments as well as recurring expenses into account. The single-time investment goes into tooling and mold manufacturing in die casting. And recurring parts include raw materials, labor, and finishing operations.
One-Time Cost: Tooling and Mold (How to Estimate It?)
Tooling cost involves a significant initial investment. Manufacturers mostly handle it as a one-time upfront cost or amortize the amount over the unit price of the parts produced.
There’s a simple method to estimate the per-part cost. You can divide the tooling cost by the expected production volume (or total tool life in shots) Mathematically speaking –
Tooling Amortization Per Part = Tooling Cost / Expected Volume (or Tool Life in Shots)
You can receive an accurate quote from the supplier with certain RFQ (Request for Quotation) inputs. Mention –
- Part Specifications: Part size, projected area, alloy type, and wall thickness.
- Mold Complexity: Cavity count, side actions (slides, cores, or threads), and tolerance/surface finish requirements.
- Production Needs: Target tool life and any specific cooling or ejection constraints.
From a practical standpoint, tooling costs can vary widely, from several thousand dollars to six figures. And the change comes from the tool’s size, complexity, and the number of cavities.
The amortization usually results in a small per-part cost in high-volume production runs. Conversely, tooling remains the primary cost driver in small-volume production.
Die Casting Part Cost Analysis
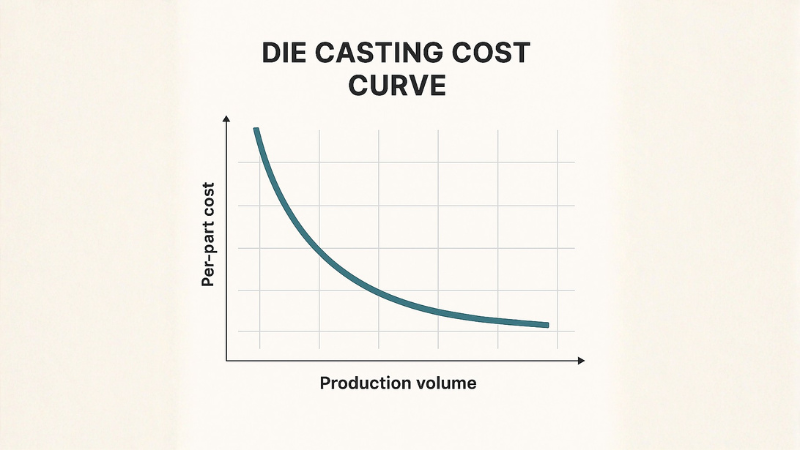
Tooling cost remains at the top for production runs under 5,000 parts. A small aluminum component may cost $10 – 20 per part in a low-volume run.
But it can plunge to $2 – 3 per part in a high-volume production. Alternative methods like CNC or sand casting seem more economical in such cases.
Costs begin to balance between tooling and recurring expenses in medium-volume production (10,000 – 50,000 parts). Per-part costs range from $3 to $8, depending on material and finishing specifications.
Tooling costs are fully amortized in high-volume production (100,000+ parts). The high scalability drives down the per-part costs. Per-part expenses can drop to $1 – 2 for small-sized zinc die-cast components.
China-made smartphone housings cost under $1.50 per part for volumes exceeding 500,000 units. Multi-cavity molds and automated finishing heavily contribute to the massive drop in pricing.
The initial cost curve is rather steep. A move from 1,000 to 10,000 can reduce per-part cost by 50 – 70%. Beyond 100,000 parts, savings plateau, but automation and optimized cycle times continue to improve.
Post-Processing Cost Analysis in Die Casting
The manufactured parts must meet dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and functional requirements. That’s where manufacturers extensively rely on specific post-processing techniques.
Die casting surely produces near-net-shape components. Still, most of those parts require machining, finishing, or coating. Those operations consume a significant portion of the total part cost.
- Machining Costs
Machining includes trimming, drilling, tapping, milling, and CNC finishing. Costs vary depending on tolerance requirements, part complexity, and machine time.
CNC machining can add $0.50 – $5.00 per part, depending on the required precision. Aerospace parts with ±0.01 mm tolerances may see machining costs exceed 20% of the total.
- Surface Treatment Costs
Surface treatments improve durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics. However, such costs vary widely depending on the process and industry requirements.
- Sand Blasting
It removes the burrs, flash, and surface impurities, creating a uniform matte finish. And you’ll have to spend $0.10 – $0.50 per part, depending on size and complexity.
- Polishing
It grants smooth and reflective surfaces for cosmetic or functional needs. Manual polishing can induce $0.50 – $2.00 per part, especially for visible consumer electronics housings.
- Anodizing
The electrochemical process enhances corrosion resistance with decorative coloring. It requires $0.30 – $1.50 per part, depending on thickness and color requirements.
- Painting, Plating, and Other Coatings
Painting adds $0.20 – $1.00 per part, depending on coating type and application method. Powder coats provide a durable finish, costing $0.50 – $2.00 per part. Electroplating (nickel, chrome) adds $1.00 – $3.00 per part in automotive and decorative applications.
Cost Saving: How to Reduce the Die Casting Cost?
Lowering the total cost without looking into performance and reliability is always a major concern. And smart cost reduction in die casting comes from decisions made before the metal touches the mold.
01. Design Optimization
Aim for uniform walls to prevent hot spots, porosity, and warpage. Such measures reduce scrap and secondary machining. A consistent geometry always lowers finishing and rework.
Consider eliminating feature(s) that require slides and/or cores unless functionally essential. Conduct DFM reviews with the foundry to catch the cost drivers. It better be done before the tooling release.
02. Reducing Secondary Machining
Integrate bosses, pads, and datum surfaces to reduce CNC operations. Choose inserts for threads for critical components. Reserve tight tolerances for functional interfaces only.
Consider broadening non-critical tolerances to cut down machining minutes and inspection time. Always match the finishing processes to product needs.
03. Right Metal Alloy to Drop Material Costs

Al alloys are ideal for automotive and electronics. Zinc alloys enable multi-cavity dies and short cycles. Magnesium gives a premium feel with higher material cost and specialized handling.
High-fluidity alloys support thin walls and intricate details to reduce machining. Stiffer alloys may simplify the tolerance control. Hedge material purchases or qualify secondary suppliers.
Aluminum Die Casting Cost Comparison: Die Casting vs Other Manufacturing Methods
Die casting is comparable to CNC machining cost, as most manufacturers opt for either one for production. Sand casting and injection molding also get preference in certain cases. It’s important for you to catch up with the cost comparison between the manufacturing processes.
Summary Comparison: Die Casting Cost Savings vs Other Methods Like CNC Machining
Die Casting is unmatched for scalable efficiency and good tolerances against expensive tooling. CNC machining excels in precision and flexibility. However, material waste and per-part costs are quite high.
Sand Casting is cost-effective for large and heavy parts that also require extensive finishing. Injection molding enables complex geometries in small parts with limited alloy choices and mechanical strength.
Experienced Aluminum Casting Manufacturer: Better Cost Control

Partnering with a well-experienced die casting manufacturer means winning in every phase. They actively help clients achieve lower costs against higher quality. Global automotive, aerospace, and electronics brands consistently rely on seasoned suppliers to balance affordability with performance.
- In-House Tools
Experienced manufacturers maintain in-house tool rooms with CNC, EDM, and heat treatment facilities. It reduces reliance on third-party suppliers, cutting lead times and avoiding markup costs.
- Engineering Support
Experienced manufacturers provide engineering support during the design phase. Clients can optimize wall thickness, draft angles, and part geometry. It further reduces tooling complexity and machining requirements.
- Quality Control Systems
Experienced manufacturers implement ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or AS9100-certified systems. They stick to strict dimensional checks, non-destructive testing, and statistical process control (SPC).
- Cost Transparency
Experienced suppliers provide clear breakdowns of tooling, material, labor, finishing, and inspection costs. Such transparency helps clients identify cost drivers and make informed trade-offs.
- Lifecycle Cost Awareness
Transparent suppliers highlight not just upfront costs but also the total cost of ownership (TCO). It includes mold maintenance, scrap rates, and energy consumption for a better understanding.
FAQs
What factors influence die casting cost the most?
Tooling, material choice, production volume, part complexity, and finishing operations are the biggest cost drivers.
Why is tooling the largest upfront expense in die casting?
Tooling requires precision machining, hardened steel, and cooling systems. Though expensive, it lasts 100,000–1,000,000 shots, making it cost-effective at scale.
What is the average per-part cost in die casting?
Per-part costs vary from $10 to $20 in low-volume runs to $1 to $2 in high-volume production. The actual price depends on alloy and finishing.
What role does part design play in die casting cost?
Complex geometries, thin walls, and tight tolerances increase tooling and scrap rates. Design for manufacturability (DFM) effectively reduces costs.
What is the difference between die casting and CNC machining costs?
Die casting is cheaper at high volumes due to low material waste. Meanwhile, CNC machining is better for low-volume, high-precision parts.
Conclusion
Die casting becomes usable and profitable only when you balance between the cost and the quality. Each key factor driving the cost estimation involves a detailed analysis beforehand by experts. Skipping the guesswork on die casting cost estimation must take place based on real-time facts. Businesses can make informed choices to maximize efficiency, reduce waste, and unlock long-term savings.
Cost-Efficient Die Casting for Top-Quality Metal Alloys at HONJENNY
Honjenny has led the die casting portfolio with guaranteed satisfaction for about 30 years. We specialize in delivering top-tier die-cast parts for minimal costs. Contact us to know more about the services.



