Introduction
The industrial sector is changing remarkably in the fast-paced technologically driven age of today. With its amazing adaptability and inventiveness, 3D printing technology is rapidly rising in prominence in the rush of modern change. It is now more than simply a new technology; it’s a strong engine pushing quick prototyping.
Simple yet sophisticated, 3D printing principles enable the quick transformation of computer designs into physical objects. This quality creates new opportunities in many different sectors, especially in the field of Rapid Prototyping, where 3D Printing is progressively turning into a necessary instrument. What then precisely makes this technology so appealing in the context of prototype manufacture?
This paper will explore the basic ideas of 3D printing, show its wide uses in Rapid Prototyping, and examine the difficulties the technology faces together with their solutions. By means of this research, we will together look at how 3D printing is guiding the manufacturing sector toward an even more creative future.
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-TDn25K-Jh4[/embedyt]
3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping
The Basic Principles of 3D Printing
The basic ideas of 3D printing are the slow building of three-dimensional objects by layer-by- layer material stacking. This technology’s fundamental idea is to turn computer designs into physical products, therefore bridging the virtual to the actual gap. The fundamental ideas of 3D printing are presented here:
Digital Design and Modeling
Digital design starts the 3-D printing process. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools first produce a virtual model. Simple geometric outlines to intricate engineering components, this model can be taken in any form or structure.
Slicing
After the digital design is finished, the software divides the model into slices—thin layers. Every slice reflects a layer in the real printing process, providing the basis for 3D printing’s layer-by–layer stacking.
Printing Process
A 3D printer stacks each slice consecutively using particular materials such plastic, metal, or biological compounds during the manufacturing process. Under direction from the digital design, the printer head accurately warms or solidifies the material at each layer, joining it with the one below.
Layer-by-Layer Stacking
Layer by layer this technique is continued until the whole item is finished. Layer by layer stacking helps each layer build upon the one before it progressively turns the virtual design into a real, concrete product.
Post-Processing
Post-processing tasks include removing support structures, surface smoothing, or adding extra components could be needed once printing is finished. This guarantees that the last 3D printed good satisfies design criteria.
3D printing is a flexible and quick production technique with straightforward core concepts. Excellent flexibility for quick prototyping made possible by this layer-by- layer stacking technique helps several sectors to innovate and create more effectively.

Application of 3D Printing in Rapid Prototyping
The advent of 3D printing has given Rapid Prototyping fresh life and quickly turned creative ideas into real-world prototypes, therefore revolutionizing several sectors. Key uses of 3D printing in rapid prototyping are listed here:
Rapid Iterative Design
While 3D printing can create excellent prototypes in a short period of time, traditional prototype manufacturing sometimes requires significant effort and money. Rapid iterations allow designers and engineers to quickly validate several design ideas, therefore accelerating the cycle of product development.
Customized Prototype Production
3D printing makes it possible to create quite personalized prototypes fit for specific requirements. In sectors including healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods—where tailored products are in demand—this is especially important. Customized prototypes printed fast by manufacturers depending on particular client needs will offer more individualized solutions.
Realization of Complex Structures
Overcoming constraints sometimes encountered by conventional manufacturing techniques, 3D Printing’s layer-by- layer stacking concept allows it to effortlessly build complicated structures and geometric patterns. This gives designers more creative space to investigate more sophisticated and original ideas.
Cost Efficiency
Often more cost-effective than conventional prototype manufacturing is 3D printing. Lowering of manufacturing cycles and material waste lets companies get better prototypes at less cost, therefore lowering the expenses related to innovation.
Education and Research
3D printing provides a perfect stage for students and researchers in the domains of education and research to evaluate design ideas. The fast development of physical models helps to grasp theoretical ideas, hence boosting scientific and academic progress.
The broad use of 3D printing in Rapid Prototyping not only improves the effectiveness of product development but also increases the limits of invention. This technology’s adaptability and efficiency create new opportunities in many different sectors, therefore promoting developments in front-edge design and manufacturing.
Technical Challenges and Breakthroughs
Although 3D printing in rapid prototyping offers great benefits, it also presents a number of technical difficulties. Nonetheless, scientists and engineers are continuously trying to overcome these obstacles, hence driving ongoing 3D printing technological innovations.
Printing Speed and Efficiency
Particularly for big and complicated constructions, the rather sluggish production speed of 3D printing can be a constraint. By means of print head design optimization, printing material improvement, and parallel printing technique implementation, researchers have effectively raised printing speed and efficiency.
Material Selection and Multi-material Printing
The spectrum of printing materials that is now accessible is small, hence multi-material printing still presents a challenging task. New printing materials—including composite materials with unique qualities—are being developed by scientists constantly. Furthermore made possible by sophisticated 3D printing technology is the utilization of several materials inside one model.
Accuracy and Surface Quality
For some uses, surface quality and great accuracy are absolutely necessary. Further printing process optimization, higher printing resolution, and post-processing methods including heat treatment and smoothing help to improve 3D printing’s surface quality and accuracy.
Large-scale Printing and Architectural Applications
Printing big items like architectural buildings still presents a technical difficulty. To handle this issue, researchers are investigating novel large-scale printing technologies like laser-based large-scale printing systems and cooperative robotic systems.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Concerns include trash creation and the effects materials used in the 3D printing process have on the surroundings. To minimize environmental impact, researchers are actively looking for more sustainable printing materials and best ways to recycle and reuse existing ones.
3D printing technology is developing remarkably and creating new opportunities for more general uses by regularly conquering these technical difficulties. These discoveries open the path for ongoing development of 3D printing in Rapid Prototyping and other domains.
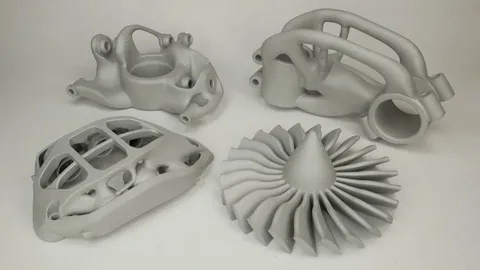
Future Prospects
The explosive growth of 3D printing portends a time of invention and possibilities. Expanding on the basis of conquering technological obstacles, 3D printing technology is likely to develop even more in the next years and become ever more important in manufacturing and other fields.
Ubiquity and Personalized Manufacturing
An era when more people and small enterprises would adopt 3D printing technology is predicted as it develops. Personalized manufacturing is projected to proliferate so that consumers may quickly create goods catered to their particular demand in homes or businesses.
Advancement in Bioprinting
In the domains of life sciences and medicine, bioprinting is destined to be a major technological tool. Scientists might produce human tissues and organs with bioprinting in the future, therefore transforming the medical industry.
Smart Materials and Multi-functional Printing
Beyond the materials used now, 3D printing will progressively add more intelligent and responsive materials. This development will provide printed items extra characteristics including sensing, self-healing, and adaptive features.
Large-scale Construction and Infrastructure Projects
In the domains of architecture and infrastructure, 3D printing technology is projected to be applied on much larger scale. 3D printing allows architects and engineers to quickly build intricate constructions, hence increasing efficiency and lowering costs.
Transformation in Education and Training
3D printing is likely to revolutionize the field of education. Through hands-on 3D printing projects, students will be able to improve their creative and problem-solving abilities while also learning science, engineering, and design ideas more intuitively.
Comprehensive Integration in Digital Manufacturing
Closely interacting with other digital manufacturing technologies including artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things will be 3D printing. This integration will provide more clever and effective manufacturing techniques, therefore raising the degree of digitalization in the industrial sector.
All things considered, the advancement of 3D printing technology will enable a wide range of sectors, from personal creativity to mass production, therefore providing fresh opportunities for invention and environmentally friendly development. The manufacturing sector worldwide is likely to be guided towards a more flexible, intelligent, and sustainable direction by the constant evolution of this technology.
Conclusion
The effective application of 3D printing technology in Rapid Prototyping reveals its great creative possibilities. By means of the basic idea of layer-by- layer stacking, it offers industrial sector more versatile and effective solutions. Notwithstanding difficulties, the constant development of technological innovations suggests that 3D printing will have even more fascinating future.
Personalized manufacturing, bioprinting, and continuous material, speed, and precision development should all show growth forward. Leading the wave of digital production and encouraging worldwide innovation, 3D printing will continue to be The continuous development of this technology will open more opportunities for the manufacturing sector, therefore energizing our society and economic growth.
Having 27 years of professional experience, Honjenny provides a broad spectrum of manufacturing capabilities including customizing services in Die Casting, Cosmetic Packaging, CNC Precision Machining, 3D Printing, and Sheet Metal Fabrication. We meet all your prototype design and manufacturing requirements by covering several industries including Home Castings, Beauty Castings, Electronic Castings, Medical Castings, and Automobile Castings. For further information or a free, non-obligatory quotation, visit our website, https://honjenny.com.

